refractometer coefficient|coolant refractometer concentration chart : online sales Some typical refractive indices for yellow light (wavelength equal to 589 nanometres [10 −9 metre]) are the following: air, 1.0003; water, 1.333; crown glass, 1.517; dense flint glass, 1.655; and diamond, 2.417. The variation . 2 dias atrás · 1 ano. Busque por nome. +. Maria Luiza de Jesus. 26/08/1938 28/02/2024. Crucilândia. +. Carlos Roberto de Jesus. Carlão. 28/06/1952 27/02/2024. Itaúna. +. Ceci .
{plog:ftitle_list}
10. 11. 12. Next. 360p. Coroa safadinha. 2 min Carlos5043675 - 360p. milf - coroa vadia da bunda grande fodendo blog amador com. 4 min Drummerpower - 360p. novinha da .
A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an index of refraction (refractometry). The index of refraction is calculated from the observed refraction angle using Snell's law. For mixtures, the index of refraction then allows the concentration to be determined using mixing rules such as the Gladstone–Dale relation and Lorentz–Lorenz equation.The changing of a light ray’s direction (loosely called bending) when it passes through variations in matter is called refraction. Refraction is responsible for a tremendous range of optical phenomena, from the action of lenses to voice .
The refractive indices of the glasses are not only dependent on wavelength, but also upon temperature. The relationship of refractive index change to temperature change is called the . The ordinary refractive index determines the speed of a wave, or how fast it oscillates as a function of position. The extinction coefficient determines how quickly a wave decays with distance. A wave decays when . Some typical refractive indices for yellow light (wavelength equal to 589 nanometres [10 −9 metre]) are the following: air, 1.0003; water, 1.333; crown glass, 1.517; dense flint glass, 1.655; and diamond, 2.417. The variation . Refraction is a phenomenon when a ray of light traveling through a medium changes (bends) its direction upon entering into another medium. The two media are separated by an interface through which the ray enters the .
refractometer how it works
The refractive index $n$> of a transparent optical medium, also called the index of refraction, is the factor by which the phase velocity $v_\rm{ph}$> is decreased relative to the velocity of light in vacuum:Figure 1. Plane wave entering and emerging from a medium with different index of refraction. Now let us ask what happens when light enters a medium with a different index of refraction at .Calculate the index of refraction for a solid medium in which the speed of light is 2.012 × × 10 8 m/s, and identify the most likely substance, based on the previous table of indicies of refraction.
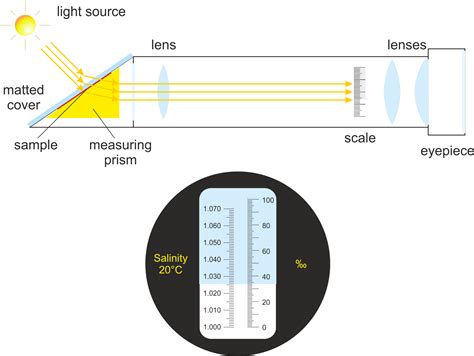
Knowledge of the actual refraction coefficient is essential in leveling surveys and precise electromagnetic distance measurement reduction. The most common method followed by the surveyor for its determination is based on the use of simultaneous reciprocal zenith observations. The commonly used formula is only an approximation valid for .Refraction at interface. Many materials have a well-characterized refractive index, but these indices often depend strongly upon the frequency of light, causing optical dispersion.Standard refractive index measurements are taken at the "yellow doublet" sodium D line, with a wavelength (λ) of 589 nanometers. There are also weaker dependencies on temperature, . Discover the step-by-step process of using a refractometer for accurate measurements. From understanding its function to maintaining its accuracy, this guide covers everything you need to know.. Understanding Refractometers. Refractometers are essential tools used in various industries, such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and automotive, .Interspecimen comparison of the refractive index of fused silica, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 55, 1205-1208 (1965) 2) C. Z. Tan. Determination of refractive index of silica glass for infrared wavelengths by IR spectroscopy, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 223, 158-163 (1998)
The influence of temperature upon the refractive index of a medium is characterized by its thermo-optic coefficient, dn/dT, i.e. the change of refractive index per degree Celsius. This particular point will be treated in Section 1.2. Pressure . Ask the Chatbot a Question Ask the Chatbot a Question refractive index, measure of the bending of a ray of light when passing from one medium into another. If i is the angle of incidence of a ray in vacuum (angle between the incoming ray and the perpendicular to the surface of a medium, called the normal) and r is the angle of refraction (angle between .10 6 .
Refractive Index and the Speed of Light cnk kn /( ) ( / )/ Note: often people don’t write the subscript 0 on c, even when they mean c 0. The speed of light is /k.Since k becomes nk in a medium, where c 0 is the speed of light in vacuum. nc c 0 / The refractive index, n, of a medium is thus the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the medium. Use the Sellmeier equation calculator to estimate the relationship between refractive index and wavelength based on Sellmeier's coefficients. The tool uses the empirical expression, meaning that you should obtain all constants from an experiment or check the Sellmeier coefficients database.
The temperature coefficient of the refractive index or the thermo-optic coefficient (dn/dt) refers to the variation of the refractive index with the temperature at a constant pressure . The dependence of air refractive index on temperature distribution has been recognized in many natural phenomena such as mirage, deformation of images observed .
A ray of light being refracted in a plastic block. In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. [1] Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomenon, but other waves such as sound waves and water waves also experience .PCE Instruments carries a number of refractometer models including portable or handheld refractometer, digital refractometer and Abbe refractometer products used in food processing, canning, beekeeping, brewing, winemaking, distilling, pharmaceutical, manufacturing, machining, . When the correction coefficient is determined, the measurements . refraction, in physics, the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another caused by its change in speed. For example, waves travel faster in deep water than in shallow. If an ocean wave approaches a beach obliquely, the part of the wave farther from the beach will move faster than the part closer in, and so the wave will swing around until it moves .
The most general form of Cauchy's equation is = + + +,where n is the refractive index, λ is the wavelength, A, B, C, etc., are coefficients that can be determined for a material by fitting the equation to measured refractive indices at known wavelengths. The coefficients are usually quoted for λ as the vacuum wavelength in micrometres.. Usually, it is sufficient to use a two .No headers. We have described reflection and refraction, but of course when a ray of light encounters an interface between two transparent media, a portion of it is reflected and a portion is refracted, and it is natural to ask, even during an . In this context, n is the phase velocity ratio of light in a vacuum to that in the material, representing refraction. The extinction coefficient k measures absorption.This chapter deals with the use of methods for measuring the refractive index of optical materials. It contains five sections: The first section recalls some bases of the electromagnetic theory of light leading to the main characteristics of the index of refraction, and their consequences in geometrical optics (Snell–Descartes laws), in the spectral transmission and .
In terms of the temperature coefficient of variation, the speed of light is slower in a sample, than in a vacuum, due to absorption and emission of light by the atoms, as has been already stated. . refractive index will be approximately 0.0001/°C. For certain other types of sample including liquidtemperature coefficient, water based products are higher and oils and chemicals generally greatest. Typical (and very approximate) values are: Sample Temperature coefficient: Change in index/ °C Glass +0.00001 Water -0.00010 (-0.07°Brix) 50% sucrose sample (50°Brix)-0.00017 (-0.08°Brix) Edible oil -0.00040 Temperature control from a circulatorRefractometer Storage box Pipette Adjustment tool Cleaning cloth Calibration liquid 7 Automatic temperature compensation The refractive coefficient is temperature-dependent. Materials expand when they are heated (their density decreases) and contract when they cool .Normal Reflection Coefficient The reflectivity of light from a surface depends upon the angle of incidence and upon the plane of polarization of the light. The general expression for reflectivity is derivable from Fresnel's Equations.For purposes such as the calculation of reflection losses from optical instruments, it is usually sufficient to have the reflectivity at normal incidence.
The change in the speed of light is related to the indices of refraction of the media involved. In the situations shown in Figure 16.17, medium 2 has a greater index of refraction than medium 1. This difference in index of refraction means that the speed of light is less in medium 2 .Reflection Coefficients for an Air-to-Glass Interface Incidence angle, i Reflection coefficient, r 1.0.5 0-.5-1.0 r || r ┴ 0° 30° 60° 90° The two polarizations are indistinguishable at = 0° Total reflection at = 90° for both polarizations. n air 1 < n glass 1.5 Brewster’s angle Zero reflection for parallel r || =0! polarization at:
The refractive index is an important parameter in optics and electromagnetics. One common use of the refractive index is calculating the angle of a refracted wave. . is called the ordinary refractive index and the imaginary part \(\kappa\) is called the extinction coefficient. Putting this into the frequency-domain equation for a wave leads .P. E. Ciddor. Refractive index of air: new equations for the visible and near infrared, Appl. Optics 35, 1566-1573 (1996) [Calculation script (Python) - can be used to calculate the refractive index of air for specific values of humidity, temperature, pressure, and CO 2 concentration] Data
refractometer for coolant concentration
n air (λ, T, P) – 11 + 0.00367 1 °C This definition is based on a circular arc used to model the often irregularly curved path of light [Kahmen and Faig, 1988].For the Gaussian refraction coefficient k of +0.13 [e.g., Brunner, 1984] and a mean Earth radius R = 6370 km, the average refraction radius of the circular path of light is about 49,000 km. The positive sign of the refraction coefficient .
refractometer factor meaning
refractometer correction chart
is learner's permit test hard
Certificado. Consultar Certificado. Informe o número de auten.
refractometer coefficient|coolant refractometer concentration chart